-
Email: contact@locaba.sg
-
Phone +65 8876 5127
Islandwide delivery $15 – FREE from $150 order!
-
Email: contact@locaba.sg
-
Phone +65 8876 5127
The Benefits of Low-Carb Diets for Diabetics

Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It requires careful management and treatment to prevent serious health complications. While there are various approaches to managing diabetes, recent research suggests that low-carbohydrate diets can be an effective way to control blood sugar levels and improve overall health. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of low-carb diets for diabetics.
Understanding Diabetes and the Role of Carbohydrates
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels. The hormone insulin, which is produced by the pancreas, plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. In people with diabetes, insulin either isn’t produced in sufficient amounts or is not used effectively by the body. This results in hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar levels, which over time can cause damage to various organs and tissues in the body.
Carbohydrates are one of the main sources of glucose in the human diet. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. This causes blood sugar levels to rise, which triggers the release of insulin by the pancreas. In people with diabetes, the body may not produce enough insulin or may be unable to use it effectively, leading to impaired glucose metabolism. (LOCABA’s low-carb cakes and desserts are therefore diabetic-friendly.)
Types of Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. It typically develops in childhood or adolescence and requires usually lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is a condition in which the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it. It’s typically associated with lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity. Type 2 diabetes can usually be managed with lifestyle modifications, medications, and sometimes insulin therapy.
How Carbohydrates Affect Blood Sugar Levels
Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels compared to other macronutrients such as protein and fat. High-glycemic carbohydrates, such as white bread and sugary foods, cause blood sugar levels to spike rapidly. In contrast, low-glycemic carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, cause a slower and more sustained rise in blood sugar levels.
For diabetics, keeping blood sugar levels within a healthy range is crucial for preventing health complications. This is where low-carb diets can be beneficial. By reducing carbohydrate intake, diabetics can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve their overall health.
The Science Behind Low-Carb Diets for Diabetics
The benefits of low-carb diets for diabetics are supported by numerous scientific studies. Here are some of the key scientific concepts underlying the success of low-carb diets:
Ketosis and Blood Sugar Control
When carbohydrate intake is limited, the body enters a metabolic state called ketosis. During ketosis, the liver produces ketones, which are used as an alternative fuel source instead of glucose. This can help lower blood sugar levels and reduce the need for insulin in diabetics.
LOCABA’s keto-friendly desserts combine low-carb with valuable other ingredients – supporting this ketosis.
In addition to its benefits for blood sugar control, ketosis has been shown to have other health benefits as well. For example, some studies suggest that it may help improve brain function and reduce inflammation throughout the body.
Insulin Sensitivity Improvement
Insulin resistance is a hallmark of type 2 diabetes. Low-carb diets have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to use insulin more effectively and reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
One theory behind this improvement in insulin sensitivity is that low-carb diets help reduce the amount of fat in the liver and pancreas, which can interfere with insulin signaling. By reducing this fat, the body is better able to use insulin to control blood sugar levels.
Studies Supporting Low-Carb Diets for Diabetics
Several randomized controlled trials have demonstrated the efficacy of low-carb diets for improving blood sugar control and other markers of health in diabetics. One study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that a low-carb diet was more effective at improving glycemic control than a low-fat diet in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. Similarly, a study published in Diabetes Care found that a low-carb diet resulted in significantly greater reductions in HbA1c levels (a marker of long-term blood sugar control) compared to a low-fat diet.
Another study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine found that a low-carb diet was more effective at reducing cardiovascular risk factors, such as blood pressure and triglyceride levels, compared to a low-fat diet. This is particularly important for diabetics, who are at increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
Overall, the scientific evidence supports the use of low-carb diets as an effective tool for managing diabetes and improving overall health. However, it is important to work with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized nutrition plan that takes into account your specific health needs and goals.
Key Components of a Low-Carb Diet for Diabetics
When it comes to adopting a low-carb diet for diabetes management, there are a few key components to keep in mind. A low-carb diet can be an effective way to manage blood sugar levels and improve overall health for individuals with diabetes.
Besides all diabetes related aspects, as all LOCABA desserts are “no table sugar added”, they also contribute to the health of your teeth!
Macronutrient Breakdown
A typical low-carb diet restricts carbohydrate intake to 50-150 grams per day, depending on individual needs. This may equate to 10-30% of total daily caloric intake. Protein intake should be sufficient to maintain muscle mass, while fat intake can range from moderate to high. It is important to work with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to determine the appropriate macronutrient breakdown for individual needs.
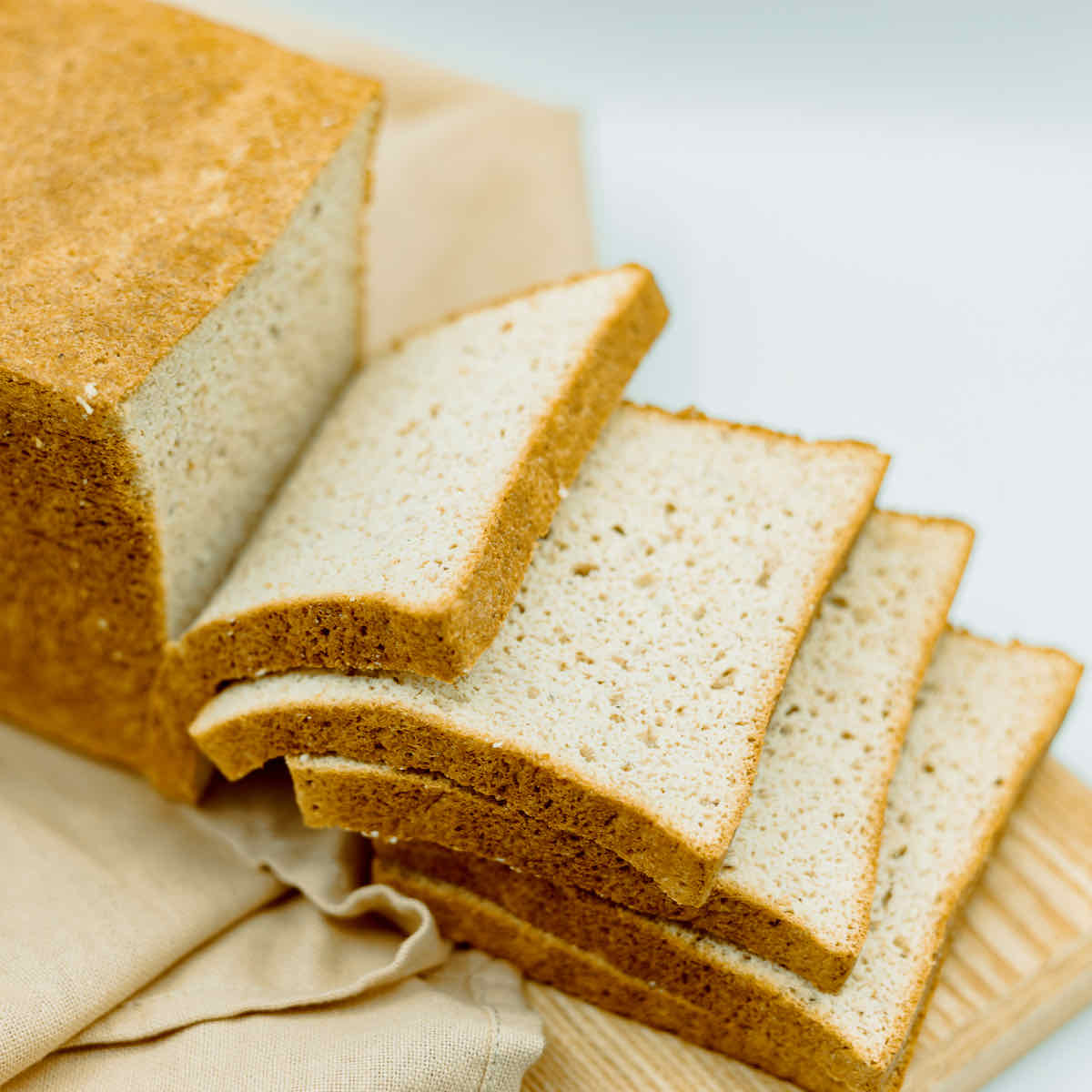
As a rough rule of thumb and according to LOCABA’s experiences if a product is under 7g carbs per 100 g, your pancreas usually ignores the carbs and thus releases no insulin at all. LOCABA’s low-carb sandwich bread (see picture above) is at 3,9 g carbs per 100 g bread!
Research has shown that a low-carb diet can improve blood sugar control and reduce the need for diabetes medication in some individuals. Additionally, a low-carb diet can lead to weight loss, improved cholesterol levels, and reduced inflammation.
Foods to Include
Low-carb diets typically emphasize whole, unprocessed foods such as meats, fish, eggs, vegetables, and nuts. A variety of low-carb fruits such as berries, avocados, and olives can also be included in moderation. These foods provide important nutrients such as protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
For example, incorporating leafy greens such as spinach and kale into meals can provide a good source of fiber and vitamins A and C. Nuts and seeds can be a great source of healthy fats and protein, while also providing important minerals such as magnesium and zinc.
Foods to Avoid
High-carb foods such as bread, pasta, rice, potatoes, and sugary foods should be avoided on a low-carb diet. Processed foods, snack foods, and sweetened beverages should also be limited or avoided altogether. These foods can cause blood sugar levels to spike and can contribute to inflammation and weight gain.
Re. rice: many products that claim to be gluten-free are produced with rice and are therefore highly glycemic and not at all diabetic-friendly. LOCABA gluten-free cakes and desserts do not contain rice to keep the carbs low.
Instead, individuals can opt for low-carb alternatives such as cauliflower rice, zucchini noodles, and almond flour bread. These alternatives can still provide the texture and flavor of traditional high-carb foods without the negative impact on blood sugar levels.
Overall, a low-carb diet can be a beneficial approach for individuals with diabetes looking to improve their health and manage their blood sugar levels. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods and avoiding high-carb and processed foods, individuals can see improvements in their blood sugar control, weight, and overall health.
Potential Health Benefits of Low-Carb Diets for Diabetics
Adopting a low-carb diet for diabetes management can offer a range of potential health benefits:
Improved Blood Sugar Control
By limiting carbohydrate intake, diabetics can help regulate their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing complications associated with high blood sugar levels.
It is important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. Simple carbohydrates, such as those found in sugary drinks and snacks, can cause blood sugar levels to spike rapidly. Complex carbohydrates, such as those found in whole grains and vegetables, are broken down more slowly and can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Weight Loss and Management
Low-carb diets have been shown to be effective for weight loss, which can be beneficial for diabetics who are overweight or obese. Weight loss can help improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of developing complications such as cardiovascular disease.
In addition to weight loss, low-carb diets can also help diabetics manage their weight in the long term. By reducing carbohydrate intake, diabetics can reduce their overall calorie intake and maintain a healthy weight.
Reduced Risk of Diabetes Complications
By improving blood sugar control, low-carb diets can help reduce the risk of developing long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as kidney disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy.
It is important for diabetics to work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor their blood sugar levels and adjust their medication as needed when following a low-carb diet.
Enhanced Energy Levels and Mental Clarity
Many people report increased energy levels and mental clarity when following a low-carb diet. This can be particularly beneficial for diabetics who may experience fatigue and cognitive impairment as a result of their condition.
Low-carb diets can also help diabetics improve their sleep quality, which can further enhance their energy levels and mental clarity.
Overall, adopting a low-carb diet can offer a range of potential health benefits for diabetics. However, it is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to ensure that the diet is safe and effective for individual needs and goals.
Conclusion
Overall, low-carb diets offer a promising approach to diabetes management. By reducing carbohydrate intake, diabetics can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve their overall health. As with any dietary approach, it’s important to work with a healthcare provider and registered dietitian to ensure adequate nutrient intake and to monitor blood sugar levels regularly. With careful attention to diet and lifestyle habits, diabetics can achieve optimal health and wellbeing.